The International Tin Association Technology team is working in both the UK and China to understand threats and opportunities to tin use. We are also building and talking to technology communities to understand and tackle key industry issues. Our work communicates a positive message about the importance of tin to daily life, now and in the future.
Most tin use sectors benefit from steady economic growth, with China still the major driver, at a long-term rate of just under 2%. There are always challenges of regulation, technology change and competition but overall tin fundamentals are robust, as tin has a wide range of uses important to modern quality of life.
More recently tin demand has been significantly impacted by macroeconomic shocks and a high-inflation environment. Markets are beginning to recover, especially in China, and there are good reasons to expect a strong rebound in 2024.
The longer-term future looks very promising, with very significant opportunities in new electronics and energy technologies opening up for tin towards 2025-2030, as outlined below.

Solders
Thanks to the positive growth forecasts for 5G-based electronics technologies in the imminent ‘4th Industrial Revolution’ as well as new markets for interconnection in electric vehicles and other climate change-related infrastructures the longer-term outlook for solder usage remains very positive, despite recent macroeconomic shocks. At the same time electronics miniaturisation that has suppressed solder markets over the last decade may weaken over the next five years, allowing for resumption of significant growth.
ITA Solder Market Report ‘Connecting Tomorrow’ 2020
ITRI Solders Technology Roadmap 2015
ITRI China Solder Technology Group

Tin Chemicals
Tin chemicals for PVC stabilisers, polymer catalysts and numerous other applications is the second largest tin use, with steady growth. They look likely to retain this position for the foreseeable future, with new uses in energy materials in prospect longer term.

Tinplate
Tinplate is mainly used in food cans as well as in some beverage cans, general line cans for chemicals, paints and dry products and also in can ends. Global consumption of tinplate remains static or declining with new opportunities in emerging economies and circular economy regulation.

Lead-Acid Batteries
Tin use in lead-acid batteries, especially in China, is expected to grow steadily with the introduction of more start-stop and microhybrid vehicles as well as growth in alternative energy and telecoms markets.

Copper Alloys & Other Uses
Copper alloys including bronze are still widely used in applications ranging from sculpture to electrical products. Tin and other alloys, including powders and coatings, are used in brake pads, roofing, engineering, bearings and numerous other ways. Traditional pewter giftware is still highly valued and tin wine capsules are used in luxury wines and spirits. There may be new opportunities for tin-copper products in electric vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure.
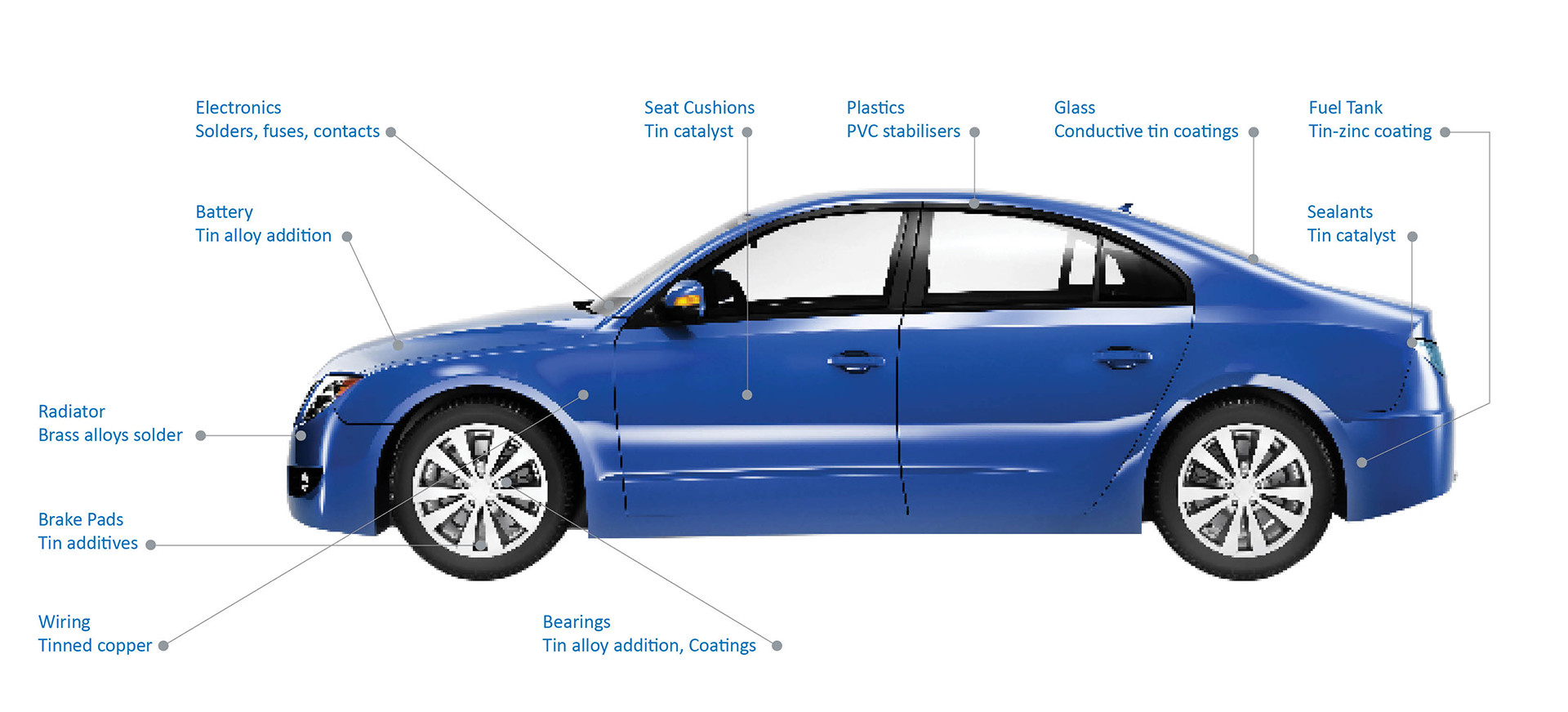
Tin Use in Vehicles
Tin is called the ‘spice element’ because a little of it is present everywhere in ways that are essential to our quality of life. Tin use in vehicles is a good example.

NEW TECHNOLOGIES
International Tin also tracks new technologies that are likely to grow future tin uses. Lithium ion batteries and other new energy materials look very promising for tin and we are working to assess their potential impact on future tin demand.

